IIF function
- Introduced in SQL Server 2012
- Returns one of two the values, depending on whether the Boolean expression evaluates to true or false
- IIF is a shorthand way for writing a CASE expression
Syntax : IIF ( boolean_expression, true_value, false_value )
Example : Returns Male as the boolean expression evaluates to TRUE
DECLARE @Gender INT SET @Gender = 1 SELECT IIF( @Gender = 1, ‘Male’, ‘Femlae’) AS Gender
Output :

Example : Using IIF() function with table data. We will use the following Employees table for this example.
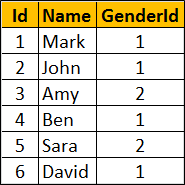
SQL Script to create Employees table
Create table Employees ( Id int primary key identity,
Name nvarchar(10),
GenderId int )
Go
Insert into Employees values (‘Mark’, 1)
Insert into Employees values (‘John’, 1)
Insert into Employees values (‘Amy’, 2)
Insert into Employees values (‘Ben’, 1)
Insert into Employees values (‘Sara’, 2)
Insert into Employees values (‘David’, 1)
Go
Write a query to display Gender along with employee Name and GenderId. We can achieve this either by using CASE or IIF.

Using CASE statement
SELECT Name, GenderId,
CASE WHEN GenderId = 1
THEN ‘Male’
ELSE ‘Female’
END AS Gender FROM Employees
Using IIF function
SELECT Name, GenderId, IIF(GenderId = 1, ‘Male’, ‘Female’) AS Gender FROM Employees





