Subquery
In Oracle, a subquery is a query within a query. You can create subqueries within your SQL statements. These subqueries can reside in the WHERE clause, the FROM clause, or the SELECT clause.
Subquery Example :
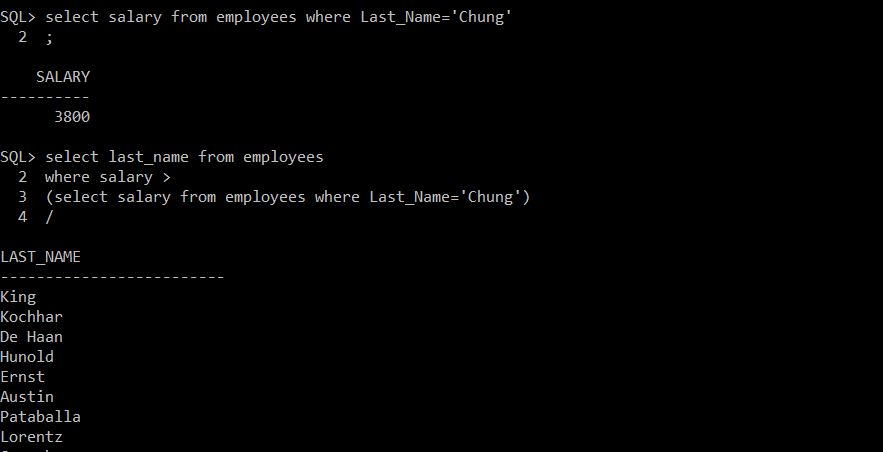
WHERE clause
Most often, the subquery will be found in the WHERE clause. These subqueries are also called nested subqueries.
For example:
SELECT *
FROM all_tables tabs
WHERE tabs.table_name IN (SELECT cols.table_name
FROM all_tab_columns cols
WHERE cols.column_name = ‘SUPPLIER_ID’);
Limitation: Oracle allows up to 255 levels of subqueries in the WHERE clause.
FROM clause
A subquery can also be found in the FROM clause. These are called inline views.
For example:
SELECT suppliers.name, subquery1.total_amt
FROM suppliers,
(SELECT supplier_id, SUM(orders.amount) AS total_amt
FROM orders
GROUP BY supplier_id) subquery1
WHERE subquery1.supplier_id = suppliers.supplier_id;
Limitations
Oracle allows an unlimited number of subqueries in the FROM clause.
FROM clause (Continue)
In this example, we’ve created a subquery in the FROM clause as follows:
(SELECT supplier_id, SUM(orders.amount) AS total_amt
FROM orders
GROUP BY supplier_id) subquery1
This subquery has been aliased with the name subquery1. This will be the name used to reference this subquery or any of its fields.
SELECT clause
A subquery can also be found in the SELECT clause.
For example:
SELECT tbls.owner, tbls.table_name,
(SELECT COUNT(column_name) AS total_columns
FROM all_tab_columns cols
WHERE cols.owner = tbls.owner
AND cols.table_name = tbls.table_name) subquery2
FROM all_tables tbls;
In this example, we’ve created a subquery in the SELECT clause as follows:
(SELECT COUNT(column_name) AS total_columns
FROM all_tab_columns cols
WHERE cols.owner = tbls.owner
AND cols.table_name = tbls.table_name) subquery2
The subquery has been aliased with the name subquery2. This will be the name used to reference this subquery or any of its fields.
The trick to placing a subquery in the select clause is that the subquery must return a single value. This is why an aggregate function such as SUM function, COUNT function, MIN function, or MAX function is commonly used in the subquery.