Linux Introduction
Linux is a community of open-source Unix-like operating systems that are based on the Linux Kernel. It was initially released by Linus Torvalds on September 17, 1991. It is a free and open-source operating system and the source code can be modified and distributed to anyone commercially or non commercially under the GNU General Public License.
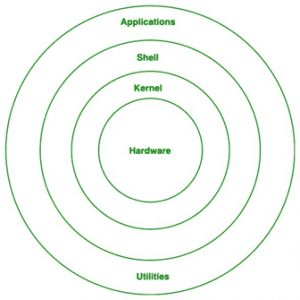
Architecture
Basic Software Installation
The APT is the tool, commonly used to install packages, remotely from the software repository. In short, it’s a simple command-based tool that you use to install files/software. The complete command is apt-get and it’s the easiest way to install files/Software packages. This easy tool informs you about packages that are currently being installed and also it informs you about the packages that are available in repositories.
1.sudo apt-get install ${packagename}
2.sudo apt-get remove ${packagename}
3.sudo apt-get update
4.sudo apt-get upgrade
5.Example: sudo apt-get install ipcalc
Unix Command Line
pwd prints working directory (prints to screen, ie displays the full path, or your location on the filesystem)
ls lists contents of current directory
ls –l lists contents of current directory with extra details
ls /home/user/*.txt lists all files in /home/user ending in .txt
cd change directory to your home directory
cd ~ change directory to your home directory
cd /scratch/user change directory to user on scratch
cd – change directory to the last directory you were in before changing to wherever you are now
mkdir mydir makes a directory called mydir
rmdir mydir removes directory called mydir. mydir must be empty
touch myfile creates a file called myfile. updates the timestamp on the file if it already exists, without modifying its contents
cp myfile myfile2 copies myfile to myfile2. if myfile2 exists, this will overwrite it!
rm myfile removes file called myfile
rm –f myfile removes myfile without asking you for confirmation. useful if using wildcards to remove files ***
cp –r dir newdir copies the whole directory dir to newdir. –r must be specified to copy directory contents recursively
rm –rf mydir this will delete directory mydir along with all its content without asking you for confirmation! ***
nano opens a text editor. see ribbon at bottom for help. ^x means CTRL-x. this will exit nano
nano new.txt opens nano editing a file called new.txt
cat new.txt displays the contents of new.txt
more new.txt displays the contents of new.txt screen by screen. spacebar to pagedown, q to quit
head new.txt displays first 10 lines of new.txt
tail new.txt displays last 10 lines of new.txt
tail –f new.txt displays the contents of a file as it grows, starting with the last 10 lines. ctrl-c to quit.
mv myfile newlocdir moves myfile into the destination directory newlocdir
mv myfile newname renames file to newname. if a file called newname exists, this will overwrite it!
mv dir subdir moves the directory called dir to the directory called subdir
mv dir newdirname renames directory dir to newdirname